FORAMINA OF SKULL AND STRUCTURES PASSING THROUGH THEM
|
Foramen |
Location |
|
1. Foramen ceacum |
The foramen situated anterior to the
crista galli in the base of skull. Usually it is blind junction of anterior
2/3rd and posterior 1/3rd of tongue where thyroglossal duct takes origin |
|
2. Foramen of monro (inter-ventricular
foramen) |
Opening of lateral ventricles into 3rd ventricle |
|
3. Foramen of Magendie |
Median opening in the roof of 4th
ventricle |
|
4. Foramen of Luschka |
Opening of lateral recesses of 4th
ventricle |
|
5. Foramen scarpa |
Incisor foramen in the oral cavity |
|
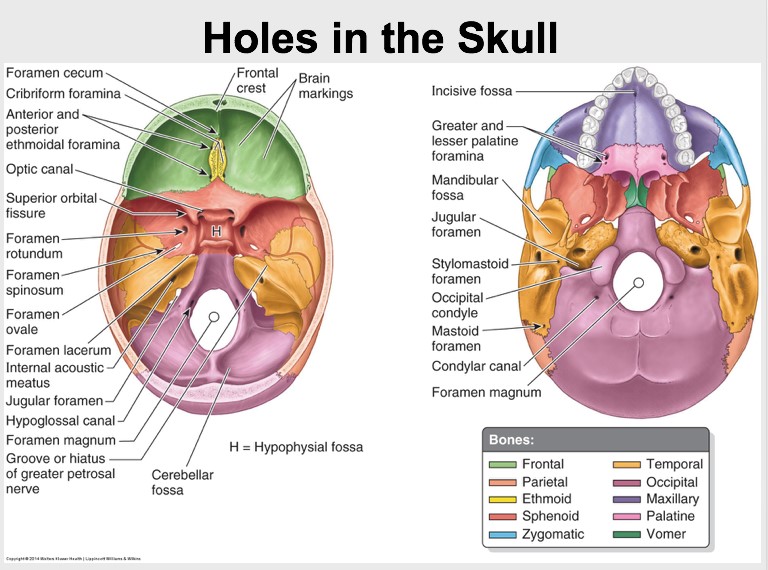
6. Foramen of ovale |
Transmits mandibular nerve and accessory
meningeal artery |
|
7. Foramen of rotundum |
Transmits maxillary nerve |
|
8. Foramen spinosum |
Transmits middle meningeal artery |
|
9. Stylomastoid foramen |
Transmits facial nerve |
|
10. Jugular foramen |
9,10, 11th cranial nerves sigmoid and
inferior petrosal sinus, internal jugular vein |
|
11. Optic canal foramen |
Optic nerve and ophthalmic artery (branch
of internal carotid artery) |
A.
Norma verticalis
Parietal foramen transmits an emissary vein from superior sagittal sinus.
B.
Norma occipitalis
Mastoid foramen transmits an emissary vein and meningeal branch of occipital artery.
C.
Norma frontalis
1. Supraorbital foramen transmits supraorbital
nerves and vessels.
2. External nasal nerve emerges between the
nasal bone and upper nasal cartilage
3. Infraorbital foramina transmits
infraorbital nerve and vessels.
4. Zygomatico facial foramen transmits the
nerve of same name.
5. Mental foramen (on mandible) transmits mental nerve and vessels.
D.
Norma lateralis
1. Tympanomastoid fissure: Transmits
auricular branch of vagus nerve
2. Mastoid foramen transmits an emissary
vein connecting the sigmoid sinus with
posterior auricular vein, meningeal branch
of occipital artery.
3. Zygomaticotemporal foramen transmits the nerve of same name and a minute artery.
E.
Norma basalis
1. Incisive foramen transmits:
a)
Terminal parts of greater palatine vessels from palate to nose.
b)
Terminal part of nasopalatine nerve from nose to palate.
2. Greater palatine foramen transmits:
Greater
palatine vessels, anterior palatine nerve.
3. Lesser palatine foramen transmits middle
and posterior palatine nerves.
4. Palatovaginal canal transmits:
a) Pharyngeal
branch from pterygopalatine ganglion.
b) Small
pharyngeal branch of maxillary artery.
5. Vomerovaginal canal: Branches of
pharyngeal nerves and vessels.
6. Foramen ovale: Mandibular nerve and
accessory meningeal artery.
7. Foramen spinosum: Middle
meningeal artery.
8. Emissary sphenoidal foramen: Transmits
an emissary vein connecting cavernous sinus with pterygoid plexus of veins.
9. Canalis innominatus: Transmits
lesser petrosal nerve.
10. Carotid canal: Transmits internal carotid artery venous and sympathetic plexus around the artery.
11. Foramen lacerum: Meningeal branch of ascending pharyngeal artery and an emissary vein from cavernous sinus, Internal carotid artery with venous and sympathetic plexus around it. In the upper part of foramen, the greater petrosal nerve unites with the deep petrosal nerve to form nerve of pterygoid canal.
12. Petrotympanic fissure: Transmits
the chorda tympanic nerve and anterior tympanic artery.
13. Foramen magnum transmits:
a) Through
wider posterior part
- Lower part of
medulla
- Tonsils of
cerebellum max
- Meninges
b) Through subarachnoid space
-Spinal accessory
nerve.
-Vertebral
arteries.
-Sympathetic
plexus around the vertebral arteries
-Anterior and posterior spinal arteries
c) Through narrow anterior part
-Apical ligament
of dens
-Membrana tectoria
14. Hypoglossal canal (HAEM): (Anterior condylar) canal transmits the hypoglossal nerve, meningeal branch of ascending pharyngeal artery, emissary vein connecting sigmoid sinus with the internal jugular, meningeal branch of hypoglossal nerve.
15. Posterior condylar canal: Transmits an emissary vein connecting the sigmoid sinus with sub-occipital venous plexus.
16. Jugular foramen:
a) Through anterior part:
- Inferior petrosal sinus
- Meningeal branch of ascending pharyngeal artery.
b) Through Middle part: 9th, 10th, 11th cranial nerves.
c) Through posterior part:
- Internal jugular vein
- Meningeal branch of occipital artery
17. Mastoid canaliculus: Transmits auricular branch of vagus nerve.
18.Tympanic canaliculus: Transmits tympanic branch of glossopharyngeal nerve to branch of glossopharyngeal nerve to middle ear.
19. Stylomastoid foramen: Facial nerve
20. Foramen caecum: Blind in nature
21. Anterior and posterior ethmoidal canals.
22. Optic canal transmits optic nerve and ophthalmic artery.
23. Superior orbital fissure transmits:
a) Lateral part: Lacrimal, frontal and trochlear nerve, superior ophthalmic vein, meningeal branch of lacrimal artery anastomosing branch of middle meningeal artery.
b) Middle part: Upper and lower divisions of oculomotor nerve with nasociliary nerve in between, abducens nerve.
c) Medial part: Inferior ophthalmic vein, sympathetic nerves from the plexus around Internal carotid artery.
24. Foramen rotundum: maxillary branch of trigeminal nerve (V2), artery of foramen rotundum, and emissary veins
25. Internal acoustic meatus: Transmits the 7th and 8th cranial nerves and labyrinthine vessels.
F. Orbit
1. Superior orbital fissure described
above.
2. Inferior orbital fissure transmits the zygomatic nerve, orbital branches of pterygopalatine ganglion, infraorbital vessels, communication between the inferior ophthalmic vein and pterygoid plexus of vein.
3. Infraorbital groove and canal transmit
the corresponding nerve and vessels,
4. Zygomatic foramen transmits the zygomatic nerve.
Worman (sutural) bones are small irregular bones found in the region of fontanelles.

