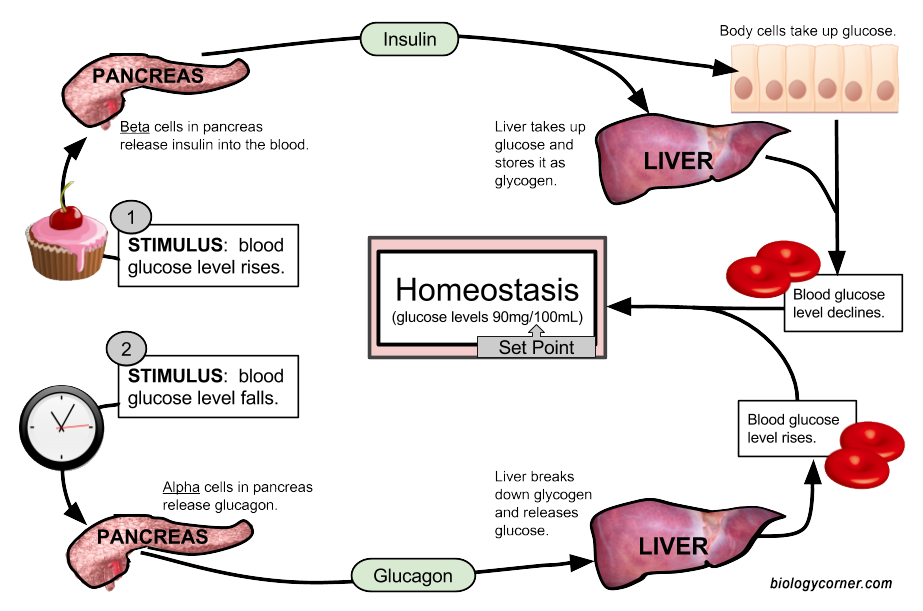
Role of Hormones in Homeostasis of Blood Glucose Levels
|
Insulin
|
Increases glycogenesis and
lipogenesis and decreases glycogenolysis and gluconeogenesis
|
Lowering of blood glucose level
|
|
Epinephrine (adrenaline)
|
Antagonizes the action of
insulin, stimulates glycogenolysis by activating phosphorylase
|
Increases blood glucose levels
|
|
Glucagon
|
Stimulates glycogenolysis by
activating liver phosphorylase and also increases gluconeogenesis
|
Increases blood glucose levels
|
|
Adrenal cortical hormone
|
Stimulates gluconeogenesis
prevents uptake of glucose by tissues
|
Increases blood glucose levels
|
|
Anterior pituitary hormone |
Lipolysis and suppression of
uptake of glucose by tissues |
Increases blood glucose levels
|
|
(ACTH, GH) thyroid hormones
|
Enhances absorption of glucose
from intestine and glycogenolysis in liver. Enhances metabolism of glucose |
Rise in blood glucose level is
transient
|